USB (Universal Serial Bus) was introduced to simplify connectivity, eliminating the clutter of serial and parallel cables. However, over the years, its evolution brought not only advancements but also challenges with multiple revisions and connector types. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the history and progression of USB, examining its impact and why it hasn’t yet delivered on the promise of a universal connection.
The Origin of USB
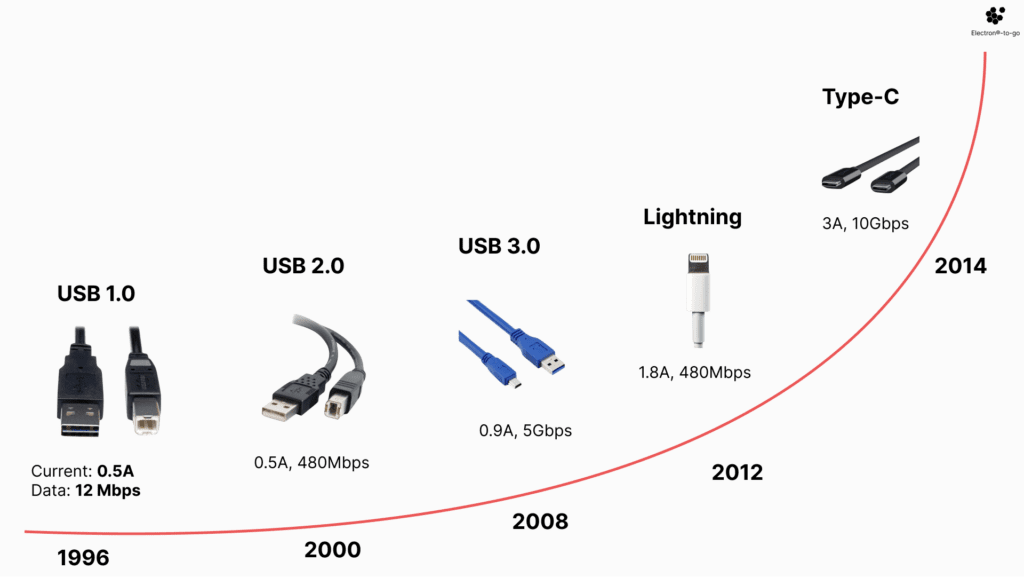
USB 1.0 debuted in January 1996, promising data transfer speeds of 12 Mbps. A consortium of seven companies spearheaded its development, aiming to make peripheral connections easier. Before USB, PCs relied on slower, less convenient serial and parallel connections.
To ensure USB’s success, the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) was established. This non-profit organization managed compliance, promoted the architecture, and enforced standards. Companies funded USB-IF through licensing fees, such as $5,000 annually for vendor IDs and $3,500 for logo usage.
USB 1.1: The First Major Update
USB 1.1, released in 1998, addressed initial issues like timing and power supply limitations. This revision gained traction, with the introduction of legacy-free PCs, where USB began replacing older ports.
However, users encountered a key design challenge: Type A and Type B connectors. The Type A connector was for the host device (e.g., a computer), while Type B was for peripherals (e.g., printers). This distinction prevented short circuits by ensuring hosts couldn’t connect directly.
A notable feature of USB was its orientation design. Plugging in a USB cable correctly often required trial and error. A simple tip: ensure the USB logo is facing upward when connecting to a horizontal port.
USB 2.0: Faster Speeds and Mini Connectors
In 2000, USB 2.0 arrived, offering speeds up to 480 Mbps, revolutionizing connectivity. Alongside this upgrade, the Mini B connector was introduced, catering to smaller devices like cameras and mobile phones.
The rise of portable electronics emphasized the need for compact and versatile connectors. USB 2.0 also enabled peripherals to rely on host devices for power and communication, simplifying designs.
USB On-The-Go (OTG)
The USB On-The-Go (OTG) specification, released in 2001, addressed the need for devices to switch roles between host and peripheral. A new Mini AB receptacle allowed devices like PDAs or printers to act as either a host or a slave.
The Mini AB receptacle had an additional ID pin, enabling the device to detect its role based on the connected plug (Mini A for host, Mini B for peripheral).
The Shift to Micro USB
By 2007, the need for an even smaller, more durable connector became evident. Enter Micro USB, introduced in USB 2.0 Revision 1.01. It addressed the growing demand for:
- Compact designs for thin devices.
- Rugged connectors with a lifespan exceeding 10,000 cycles (double that of Mini USB).
- Reduced mechanical strain on the port.
Micro USB featured spring-loaded latches to secure the connection, minimizing stress on the device’s socket.
The Role of Industry Leaders
The transition to Micro USB wasn’t just about technical advancements. Industry leaders like Nokia played a significant role in shaping its adoption. Faced with competition from Apple’s iPhone, Nokia sought to modernize its designs. Phones like the Nokia 8600 Luna incorporated Micro USB, setting a trend for sleek, durable connectors.
The Road Ahead: USB-C and Beyond
Despite the advancements, USB didn’t stop evolving. The introduction of USB-C aimed to unify connectors across devices, offering reversible plugs, higher data speeds, and power delivery capabilities. However, the journey from USB 1.0 to USB-C highlights a recurring challenge: balancing innovation with standardization.
Conclusion
USB revolutionized connectivity, transforming how devices communicate. From its inception in 1996 to the introduction of Micro USB, each iteration addressed specific technological and market needs. While USB hasn’t fully realized the dream of a single universal connector, it has undoubtedly brought us closer to a more connected world.
For a deeper understanding of USB’s evolution and its impact, refer to this article as your comprehensive guide.
Tags:
USB history, USB evolution, Micro USB vs Mini USB, USB OTG explained, USB 2.0 features, Universal Serial Bus, USB connectors
Hashtags:
#USB #TechHistory #MicroUSB #MiniUSB #USBEvolution #Connectivity #USBOTG