In the world of graphic design, understanding the difference between raster images and vector graphics is crucial. These two formats have unique characteristics that influence how they are used, manipulated, and displayed in projects. This article delves into the distinctions between raster images and vectors, explaining their composition, applications, and advantages.

What Are Raster Images?
Raster images, also known as bitmap images, are composed of tiny squares called pixels. Each pixel contains information about color, brightness, and clarity, collectively forming the entire image. Raster images are widely used for photographs and digital artworks but have limitations in scalability.
Characteristics of Raster Images
- Pixel Composition:
Raster images are formed by a grid of pixels, where each pixel is a small square of color. - Resolution Dependency:
The clarity of raster images depends on their resolution, measured in DPI (dots per inch). High-resolution images have more pixels per inch, resulting in greater detail. - Scaling Issues:
When a raster image is enlarged, the individual pixels become visible, leading to pixelation and loss of quality. For example, zooming into a JPEG or PNG file reveals a grid-like structure.
Common Raster Formats
- JPEG
- PNG
- GIF
- TIFF
What Are Vector Graphics?
Vector graphics are created using mathematical equations and geometric elements such as points, lines, and curves. Unlike raster images, vectors are resolution-independent, meaning they can be scaled infinitely without losing quality.
Characteristics of Vector Graphics
- Mathematical Basis:
Vectors are defined by mathematical calculations, allowing shapes and lines to maintain sharpness at any size. - Scalability:
You can enlarge a vector graphic to the size of a billboard or reduce it to a postage stamp without compromising its quality. - Editability:
Vector graphics consist of individual elements that can be edited independently. For example, you can change the color or shape of a specific part without affecting the rest of the design.
Common Vector Formats
- SVG
- EPS
- AI
- PDF (vector-based)
Key Differences Between Raster Images and Vector Graphics
| Feature | Raster Images | Vector Graphics |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pixels | Mathematical equations |
| Scalability | Loses quality when enlarged | Maintains quality at any size |
| File Size | Larger, especially at high resolution | Typically smaller |
| Editability | Limited | Highly editable |
| Applications | Photographs, web images | Logos, icons, technical drawings |
Why Use Vector Graphics?
Vector graphics are preferred for certain applications due to their versatility and scalability:
- Logo Design: Logos often need to be resized for various uses, making vectors the ideal choice.
- Printing: From small brochures to large banners, vector graphics ensure sharp prints.
- Machine Readability: Vectors are essential for tasks like embroidery or cutting, where machines follow the paths defined in the graphic.
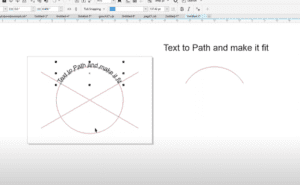
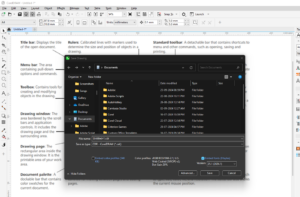
Practical Example: Editing a Vector in CorelDRAW
To understand how vectors work, let’s examine an editable vector in CorelDRAW:
- Zoom In Without Quality Loss:
Enlarge a vector graphic, and you’ll notice that it retains its sharpness, unlike raster images. - Manipulate Elements:
Ungroup the elements of the vector graphic to edit each part individually. For instance, you can change the color or shape of a specific element. - Path Adjustments:
Using tools like the shape tool, adjust the control points of a vector. The software calculates the adjustments dynamically, ensuring smooth transitions.
Applications of Raster Images and Vectors
Both formats have their unique advantages:
- Use raster images for digital photos, web graphics, and detailed visual content.
- Opt for vector graphics for logos, icons, and any design requiring scalability and precision.
Understanding when to use each format will help you create more efficient and visually appealing designs.
Conclusion
Both raster images and vector graphics play integral roles in design projects. While raster images excel in detailed visuals like photographs, vector graphics shine in scalability and precision. Learning to leverage both formats will greatly enhance your design capabilities.
Tags and Hashtags
Tags: raster images, vector graphics, CorelDRAW, bitmap images, scalable graphics, design tips, graphic design basics, DPI, pixelation, resolution-independent
Hashtags: #RasterImages #VectorGraphics #CorelDRAW #GraphicDesign #DesignTips #ScalableGraphics #BitmapVsVector #DPI