Have you ever wondered what hidden information your photos might contain? Beyond what’s visible to the naked eye, images can reveal GPS locations, device details, and even personal identities—making them a goldmine for cybersecurity professionals, journalists, and ethical hackers.
In this article, we’ll explore three powerful techniques to extract hidden data from images:
- Metadata Extraction – Uncover camera details, timestamps, and even GPS coordinates.
- Reverse Image Search – Track down the origin of an image or detect manipulated photos.
- Facial Recognition & AI Analysis – Identify people and objects using advanced tools.
Let’s dive in!
1. Extracting Metadata: The Digital DNA of Photos
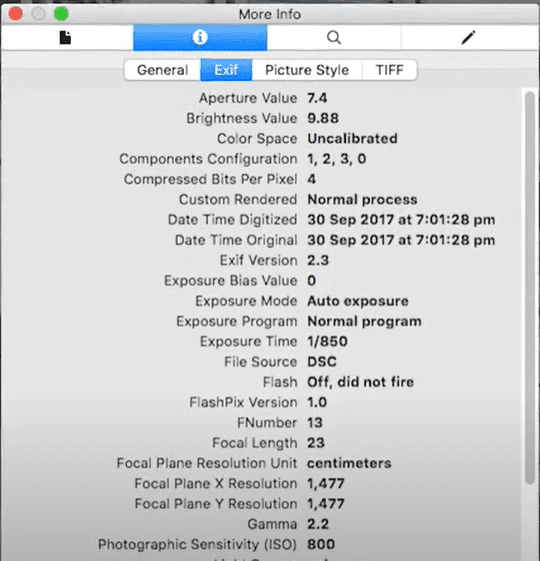
Every image file contains metadata—hidden information stored by cameras, smartphones, and editing software. This can include:
- Camera model & settings (shutter speed, aperture).
- Date & time the photo was taken.
- GPS coordinates (if location services were enabled).
How to Extract Metadata
Method 1: Using ExifTool (Command Line)
If you’re using Kali Linux (or any Linux distro), run:
exiftool -H filename.jpg
This reveals all embedded metadata in a structured format.
Method 2: Online Tools (GUI-Based)
For a user-friendly approach, try:
- Jeffrey’s Exif Viewer (drag & drop images).
- Metapicz (visualizes GPS data on a map).
⚠️ Warning:
- Social media platforms (Instagram, Facebook) strip metadata for privacy.
- Email attachments & personal uploads may still contain sensitive data.
2. Reverse Image Search: Finding the Origin of a Photo
Ever found an image online and wondered where it came from? Reverse image search helps:
✔ Verify authenticity (detect deepfakes or edited images).
✔ Track down original sources (useful for journalists).
✔ Identify locations or objects in an unknown photo.
Best Tools for Reverse Image Search
| Tool | Best For |
|---|---|
| Google Images | General searches, finding similar images |
| TinEye | Tracking image reuse across the web |
| Yandex Images | Often finds matches Google misses |
How to Use:
- Go to Google Images.
- Click the camera icon (Search by Image).
- Upload the photo or paste its URL.
3. Facial Recognition & AI-Powered Image Analysis
What if you could search the web using just a face? AI-powered tools make it possible.
A) Facial Recognition (Finding People Online)
- PimEyes – Scans the web for matching faces.
- FaceCheck.ID – Useful for OSINT investigations.
Limitations:
- Some results require a paid subscription.
- Ethical concerns – always use responsibly.
B) AI Object & Text Recognition
Tools like:
- Google Vision AI – Identifies objects, landmarks, and text.
- Microsoft Azure Computer Vision – Extracts text (OCR) and analyzes scenes.
Example:
- Upload a street sign photo → AI extracts the text.
- Submit a landmark image → AI pinpoints its location.
Ethical Considerations & Cybersecurity Risks
While these techniques are powerful, they come with risks:
🔴 Hackers can exploit metadata for phishing or social engineering.
🔴 Facial recognition raises privacy concerns.
🔴 Reverse image searches can expose personal info.
✅ Always use these tools ethically & legally.
Final Thoughts
Images hold far more data than we realize. Whether you’re:
- A journalist verifying sources,
- A cybersecurity expert investigating threats, or
- A privacy-conscious individual,
Understanding image forensics is crucial in today’s digital world.
Want to learn more about OSINT or ethical hacking? Let us know in the comments!
Tags:
image forensics, metadata extraction, reverse image search, facial recognition, OSINT, cybersecurity, ethical hacking, photo analysis, privacy protection
Hashtags:
#ImageForensics #OSINT #CyberSecurity #ReverseImageSearch #Metadata #Privacy #EthicalHacking #DigitalInvestigations #TechTips