In our digital world, every photo tells more of a story than what’s visible to the naked eye. Images contain layers of hidden data that can reveal locations, devices used, and even help identify individuals. This guide explores professional techniques used in cybersecurity, digital forensics, and open-source intelligence (OSINT) to extract valuable information from images.

1. Extracting Metadata: The Digital DNA of Images
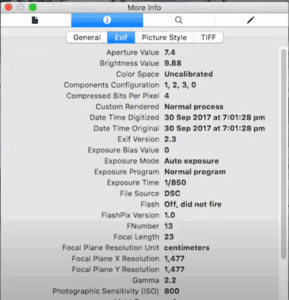
What is Image Metadata?
Metadata is embedded information stored within image files that can include:
- Camera make and model
- Date and time of capture
- GPS coordinates (if location services were enabled)
- Software used for editing
- Copyright information
Tools for Metadata Extraction
1. ExifTool (Command Line)
A powerful open-source tool available on Kali Linux and other distributions.
Installation:
sudo apt-get install exiftoolBasic Usage:
exiftool -H filename.jpgKey Features:
- Extracts EXIF, IPTC, and XMP metadata
- Can batch process multiple files
- Outputs in various formats (JSON, CSV, HTML)
2. Jeffrey’s Image Metadata Viewer (Online)
For those who prefer a graphical interface, this web-based tool provides a clean visualization of metadata.
How to Use:
- Visit Jeffrey’s Image Metadata Viewer
- Upload your image
- View organized metadata including GPS coordinates on a map
Security Implications
- Privacy Risk: Photos shared directly via email or cloud storage often retain metadata
- Protection Methods:
- Use built-in OS tools (Windows: Right-click > Properties > Remove Properties)
- Tools like MAT2 for metadata cleaning
2. Reverse Image Search: Tracing an Image’s Origin
Top Reverse Image Search Engines
| Tool | Best For | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Google Images | General searches | images.google.com |
| TinEye | Finding older versions | tineye.com |
| Yandex Images | Russian/European content | yandex.com/images |
| Bing Visual Search | Microsoft ecosystem | bing.com/visualsearch |
Advanced Techniques
- Crop Searching: Isolate key elements before searching
- Color Filtering: Use dominant colors as search parameters
- Temporal Analysis: Check archive.org for historical versions
3. AI-Powered Image Analysis
Cutting-Edge Tools
Google Vision AI
- Identifies objects, landmarks, and text
- Estimates emotional expressions
- Detects inappropriate content
Try it: Cloud Vision API
Microsoft Azure Computer Vision
- Detailed image description generation
- Celebrity recognition
- Handwritten text extraction
Demo: Azure Computer Vision
Practical Applications
- Journalism: Verifying user-submitted content
- Law Enforcement: Identifying locations from partial images
- Business Intelligence: Monitoring brand logo usage
4. Facial Recognition & Person Search
Leading Facial Recognition Tools
| Tool | Accuracy | Cost | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| PimEyes | High | Paid | pimeyes.com |
| Face++ | Enterprise-grade | API-based | faceplusplus.com |
| Betaface | Detailed analysis | Freemium | betaface.com |
Ethical Considerations
- Consent Requirements: Varies by jurisdiction (GDPR in EU)
- False Positives: Current systems have 1-5% error rates
- Bias Issues: Performance varies across demographics
5. Practical OSINT Workflow
Step-by-Step Investigation:
- Metadata Extraction: Gather basic information
- Reverse Search: Find online appearances
- AI Analysis: Identify objects/text
- Facial Recognition: Locate other images
- Geolocation: Cross-reference with map data
Example Case:
A journalist receives an anonymous tip with an image. Using these techniques, they:
- Extract metadata showing the photo was taken with an iPhone 13
- Reverse search finds the image on a deleted Facebook post
- Facial recognition links it to a public figure’s cousin
- GPS coordinates place the scene at a controversial construction site
Security Best Practices
For Investigators:
- Document chain of custody for legal cases
- Use virtual machines for sensitive investigations
- Maintain detailed case notes
For Personal Privacy:
- Disable geotagging in smartphone camera settings
- Use metadata scrubbers before sharing
- Be cautious with cloud photo backups
Legal Framework
- US Laws: CFAA governs unauthorized access
- EU Regulations: GDPR restricts biometric data use
- Copyright Issues: Fair use doctrines vary by country
Emerging Technologies
- Deepfake Detection: Tools like Microsoft Video Authenticator
- Neural Image Analysis: Identifying AI-generated art
- 3D Reconstruction: Building models from image sets
Learning Resources
- Courses:
- SANS FOR585: Smartphone Forensics
- OSINT Curious Project
- Books:
- “Open Source Intelligence Techniques” by Michael Bazzell
- “Digital Forensics with Open Source Tools” by Cory Altheide
Conclusion
Modern image analysis combines traditional metadata examination with advanced AI, creating powerful tools for legitimate investigations while posing significant privacy challenges. As technology evolves, so must our understanding of both its capabilities and ethical boundaries.
Tags: image forensics, metadata extraction, reverse image search, facial recognition, OSINT, cybersecurity, digital investigation, privacy protection
Hashtags: #ImageForensics #CyberSecurity #OSINT #DigitalPrivacy #Metadata #ReverseSearch #EthicalHacking #PhotoAnalysis #InfoSec #DigitalFootprint