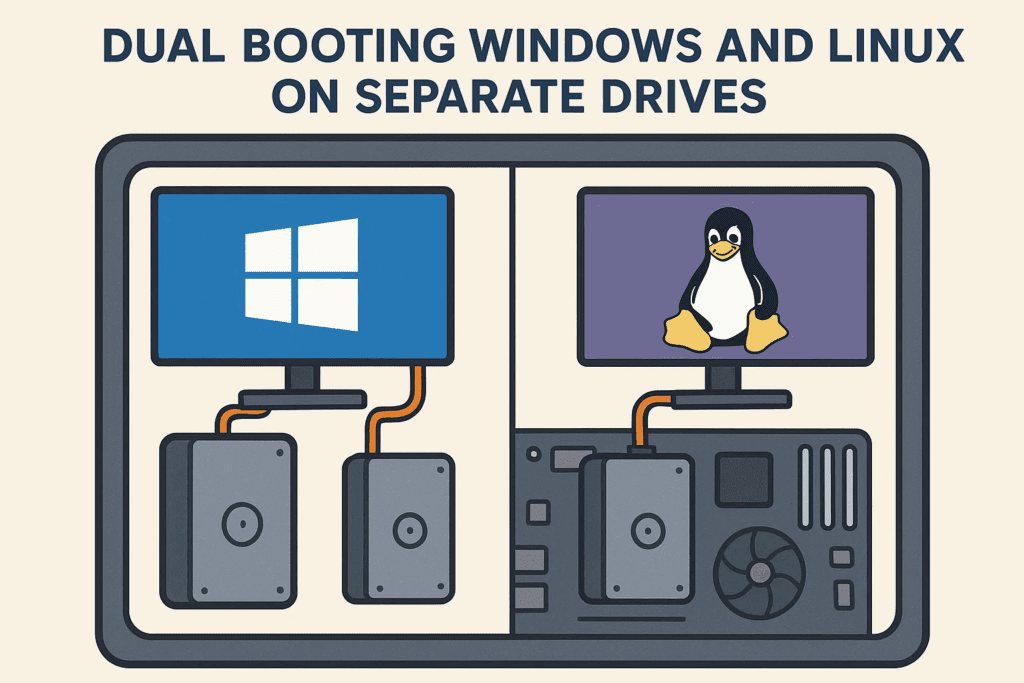
Setting up a dual-boot system with Windows and Linux is a great way to enjoy the benefits of both operating systems without compromising performance. Unlike virtualization, dual-booting gives each OS full hardware access, making it ideal for gaming, development, and productivity.
This guide covers two methods for dual-booting:
- Single-Drive Dual Boot (Linux and Windows share one drive)
- Dual-Drive Dual Boot (Each OS has its own drive)
We’ll also discuss why a dual-drive setup is better and how to avoid common pitfalls.
🛠️ Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
✅ A backup of your important data
✅ A bootable USB with your preferred Linux distro (e.g., Linux Mint)
✅ Rufus or Balena Etcher (to create the bootable USB)
✅ A second SSD/HDD (for dual-drive setup)
💽 Method 1: Single-Drive Dual Boot (Windows + Linux on One Drive)
Step 1: Boot into Linux Live USB
- Insert your Linux USB and restart your PC.
- Press BIOS key (usually
F12,F2, orDelete) to access the boot menu. - Select the USB drive (e.g., “UEFI: Corsair Voyager”) and boot into Linux.
Step 2: Install Linux Alongside Windows
- Open the Linux installer (e.g., Linux Mint’s installer).
- Select “Install Linux Mint alongside Windows Boot Manager”.
- Adjust partition sizes (drag slider to allocate space).
- Click “Install Now” and confirm.
Step 3: Reboot & Select OS via GRUB
After installation:
- GRUB bootloader appears, letting you choose between Linux or Windows.
- Default OS can be changed in GRUB settings.
⚠️ Downsides of Single-Drive Dual Boot
❌ Slower Windows boot (GRUB loads first)
❌ Risk of GRUB corruption (Windows updates can break it)
❌ Harder to remove Linux later (requires manual partition cleanup)
🔧 Method 2: Dual-Drive Dual Boot (Windows & Linux on Separate Drives)
This is the recommended method for stability and ease of use.
Option A: Physically Disconnect Windows Drive (Best for reliability)
Step 1: Disconnect Windows Drive
- Shut down your PC.
- Unplug the Windows SSD (or disable it in BIOS).
Step 2: Install Linux on Second Drive
- Boot from Linux USB.
- In the installer, select “Erase disk and install Linux” (since only the Linux drive is detected).
- Complete installation.
Step 3: Reconnect Windows Drive
- Shut down and reconnect the Windows SSD.
- Boot into BIOS (
DeleteorF2). - Set boot priority:
- 1st: Windows SSD (default)
- 2nd: Linux SSD
Now, pressing F12 at startup lets you choose between Windows and Linux without GRUB interfering.
Option B: Install Linux Without Disconnecting Windows Drive (Riskier but possible)
- Boot into Linux USB.
- In the installer, select “Something Else” (manual partitioning).
- Select the second SSD (e.g.,
/dev/sdb). - Set bootloader to install on the Linux drive (NOT the Windows drive).
- Complete installation.
⚠️ Warning: Some Linux installers still place GRUB on the Windows drive, so disconnecting is safer.
⚖️ Why Dual-Drive is Better Than Single-Drive
| Feature | Single-Drive | Dual-Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Boot Speed | Slower (GRUB loads first) | Faster (BIOS directly boots OS) |
| Stability | Risk of GRUB corruption | No GRUB interference |
| Removing Linux | Complicated (manual cleanup) | Just unplug the Linux drive |
| Windows Safety | Vulnerable to GRUB issues | Windows remains untouched |
🔧 Troubleshooting & Tips
1. Fixing GRUB if Broken
If Windows updates break GRUB:
- Boot into Linux USB → Open Terminal.
- Run:
sudo grub-install /dev/sdX # Replace X with your Linux drive
sudo update-grub2. Changing Default Boot OS in BIOS
- Enter BIOS (
Delete/F2). - Go to Boot Priority → Set preferred OS as first.
3. Removing Linux Later
- Dual-Drive: Just format the Linux SSD in Windows Disk Management.
- Single-Drive: Use a tool like GParted to delete Linux partitions and repair Windows bootloader.
🔚 Final Thoughts
A dual-drive dual-boot is the most reliable way to run Windows and Linux side by side. It avoids GRUB issues, keeps Windows safe, and makes removing Linux effortless.
For best results:
✔️ Use separate SSDs for each OS
✔️ Disconnect Windows drive during Linux install
✔️ Set boot priority in BIOS
📌 Tags:
Dual Boot, Windows and Linux, GRUB Bootloader, Linux Installation, SSD Partitioning, BIOS Settings
📢 Hashtags:
#DualBoot #Windows11 #LinuxMint #TechGuide #SSD #PCSetup #Bootloader
⚠️ Disclaimer:
- Back up your data before partitioning.
- Incorrect partitioning can lead to data loss.
- This guide assumes basic PC hardware knowledge.
Need help? Drop a comment below! 🚀