Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only. Do not attempt any of the procedures outlined here on systems or servers without explicit permission from the owner. Always conduct cybersecurity tests within legal boundaries and in safe, controlled environments.
Introduction
Understanding how insecure protocols like FTP (File Transfer Protocol) work can help us better defend against online threats. FTP is a basic method of transferring files over a network, but it lacks encryption—making data transfers, including usernames and passwords, vulnerable to interception.
This article walks you through a demonstration of FTP’s insecurity using Windows, Kali Linux, and Wireshark. The goal is to expose the risks of using unencrypted protocols and emphasize the importance of using secure alternatives like SFTP.
Step 1: Enable FTP Service on Windows
Before any demonstration can begin, you need to activate the FTP server on a Windows machine.
- Open Control Panel on your Windows computer.
- Go to Programs and Features.
- On the left panel, click on “Turn Windows features on or off.”
- Find and expand Internet Information Services (IIS).
- Expand the FTP Server option and check FTP Service.
- Click OK to begin installation—this will take just a few moments.
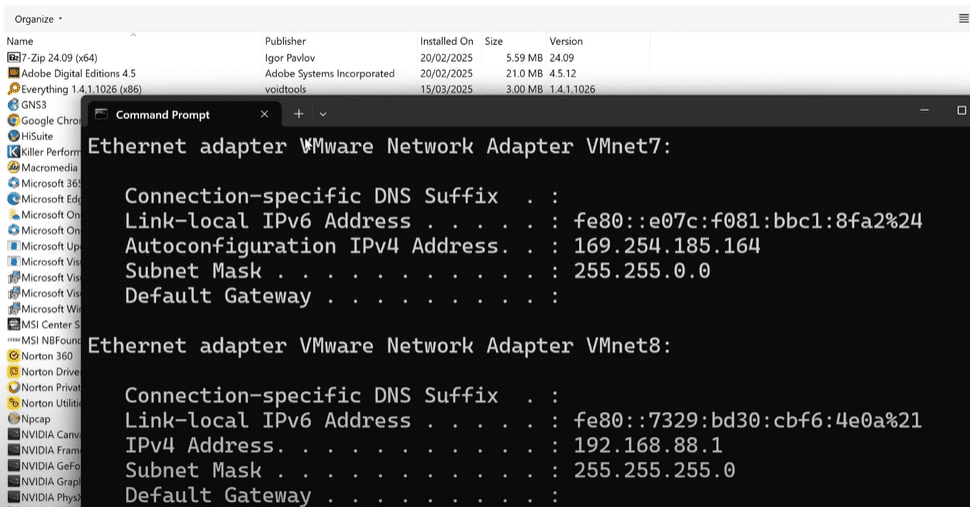
Step 2: Find Your Windows IP Address
To connect to your FTP server from another device, you’ll need the IP address of the Windows machine:
- Open Command Prompt on your Windows device.
- Type
ipconfigand press Enter. - Note the IPv4 Address listed. This is the address your FTP client will connect to.
Step 3: Connect to the FTP Server from Kali Linux
From a Kali Linux device, open the terminal and connect to the Windows FTP server:
ftp <IP address>
Replace <IP address> with the actual IP from the previous step.
You will be prompted to enter a username and password (pre-configured on the Windows FTP server). Once authenticated, you’ll gain access to the server’s file directory.
- Use the
cdcommand to navigate to the *C:* drive. - You will now be able to browse visible files on the server.
This highlights how easily accessible FTP servers can be—especially if weak credentials are used.
Step 4: Start Wireshark to Capture FTP Traffic
Now, to truly reveal the vulnerabilities of FTP, use Wireshark to capture network traffic:
- Open a terminal in Kali Linux.
- Run Wireshark with root privileges:
sudo wireshark
- In Wireshark:
- Choose the Ethernet interface (usually eth0).
- Click Capture > Start.
- Leave the capture running in the background.
While Wireshark is active, repeat the FTP login procedure:
ftp <IP address>
As you navigate through the FTP server (e.g., accessing the C drive), all traffic between the Kali Linux client and the Windows FTP server is being captured.
Step 5: Analyze Captured FTP Packets
Once done with FTP activities, return to Wireshark and stop the capture. Now let’s analyze the captured data.
- In the Wireshark filter bar, type:
tcp.port == 21
This filter isolates FTP traffic, which uses TCP port 21.
- Locate the first packet labeled as FTP.
- Right-click on it and select “Follow” > “TCP Stream”.
A new window will appear, revealing the full conversation between the client and the server. This includes sensitive details such as:
- FTP username
- FTP password
- Commands and file navigation activity
This vividly demonstrates how FTP sends data in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception.
Step 6: Secure Your Connection with SFTP
The solution to FTP’s security flaws is to avoid using FTP altogether. Instead, opt for:
- SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol): Encrypts all data, including credentials.
- FTPS (FTP Secure): FTP over SSL/TLS, which provides encryption.
Always secure your servers and systems. Avoid outdated and insecure protocols unless testing in a safe, controlled environment with permission.
Conclusion
FTP is an outdated protocol that exposes sensitive data during transmission. This demonstration clearly shows how easy it is to intercept usernames and passwords using simple tools like Wireshark. As cyber threats evolve, it’s vital to understand both the risks and how to mitigate them.
Always use secure alternatives such as SFTP, and ensure proper network security practices are followed to protect your digital environment.
Tags: ftp, sftp, wireshark, ftp vulnerability, network security, ethical hacking, kali linux, windows ftp server, cyber security, secure file transfer, wireshark tutorial, network monitoring, tcp port 21, tcp stream analysis
Hashtags: #FTP #Wireshark #NetworkSecurity #EthicalHacking #CyberSecurity #SFTP #KaliLinux #TCP #PacketSniffing #DigitalDefense