If your Windows 11 PC is acting up, crashing, or running painfully slow — don’t panic. There’s a powerful built-in troubleshooting tool that can help you identify and fix issues: Safe Mode.
Whether you’re dealing with malware, driver conflicts, or startup errors, Safe Mode provides a stripped-down environment where you can safely investigate problems and take corrective action without interference from third-party apps or services.
In this article, we’ll explore two reliable methods to boot into Safe Mode in Windows 11 — one from within Windows and another when Windows won’t even start. No shortcuts, no skipped steps — just a clear guide to help you troubleshoot like a pro.

🧠 What Is Safe Mode in Windows 11?
Before we dive into the steps, let’s understand the concept.
Safe Mode is a diagnostic startup mode in Windows that loads only essential drivers and system services, stripping out any background apps, startup programs, or third-party interference.
There are three main versions of Safe Mode:
- Safe Mode (Minimal) – Basic interface with no networking.
- Safe Mode with Networking – Adds networking drivers/services.
- Safe Mode with Command Prompt – For command-line diagnostics.
Safe Mode is used when:
- Windows is crashing or freezing
- You suspect a driver, app, or malware is causing issues
- You need to uninstall problematic software or update drivers
- Windows won’t start normally
✅ Method 1: Boot into Safe Mode from Inside Windows 11
If your PC is functional enough to log into Windows, this is the easiest method. It doesn’t require any command line or bootable USB.
Step-by-Step Guide:
Let’s walk through this method slowly. Grab a coffee if needed — we’re diving into diagnostics mode!
Step 1: Access the Recovery Menu
- Click the Start menu.
- Select the Power icon (bottom right corner).
- Hold down the Shift key on your keyboard.
- While holding Shift, click Restart.
💡 Why this works: Holding Shift while clicking Restart triggers Windows to enter the Recovery Environment (WinRE), rather than rebooting normally.
Step 2: Navigate to Startup Settings
Once your PC reboots into the blue Recovery screen:
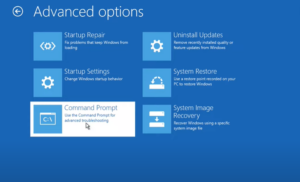
- Click Troubleshoot
- Select Advanced Options
- Click Startup Settings
- Now click Restart
Your PC will reboot again, and you’ll see a numbered list of startup options.
Step 3: Choose Your Safe Mode Option
On the Startup Settings screen, press:
- 4 to enter regular Safe Mode
- 5 for Safe Mode with Networking
- 8 to disable early launch anti-malware protection (useful if you suspect antivirus interference)
✅ We recommend pressing 4 for most basic issues.
If you need Internet (e.g., to update drivers), press 5.
Step 4: Sign In and Troubleshoot
Once you press your option key:
- Windows 11 will boot into Safe Mode
- You’ll notice a black desktop with the words “Safe Mode” in the four corners
From here, you can:
- Uninstall software or updates
- Run antivirus scans
- Check Device Manager for faulty drivers
- Use Command Prompt or System Restore tools
Step 5: Exit Safe Mode
When you’re done troubleshooting:
- Click Start > Power > Restart
- Your PC will boot back into normal Windows mode
🧯 Method 2: Enter Safe Mode When Windows 11 Won’t Start
Now let’s say your system isn’t booting properly — maybe it crashes on startup or gets stuck in a boot loop. Don’t worry — there’s still a way to enter Safe Mode using Automatic Repair.
Let’s walk through the recovery-based method.
Step 1: Trigger Automatic Repair
To do this, you’ll need to force shutdown your PC 2–3 times:
- Turn on your computer
- Once you see the Windows loading logo, hold the power button until the PC shuts off
- Repeat this 2 more times
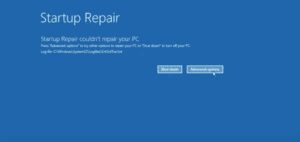
On the 3rd boot, you should see a screen that says:
“Preparing Automatic Repair”
If successful, it will take you to a screen with Advanced Options.
Step 2: Access Startup Settings
Once on the “Automatic Repair” screen:
- Click Advanced Options
- Choose Troubleshoot
- Go to Advanced Options again
- Click Startup Settings
- Then hit Restart
Now your PC will reboot again and show the Startup Settings screen.
Step 3: Choose Your Safe Mode
Just like in Method 1:
- Press 4 for regular Safe Mode
- Press 5 for Safe Mode with Networking
Your system will now enter Safe Mode, even if it couldn’t boot before. This is helpful for fixing malware infections, driver issues, or corrupted startup files.
You might be intrested in these topics too!
- 9 Windows Settings You Should Never Disable: Keep Your PC Safe and Efficient
- Fixyfier: The All-in-One Free Windows Repair Tool for Everyone
- The Ultimate Guide to Troubleshooting 30 Common Desktop PC Problems
- 5 Best Way to Automatic Repair Loop and “Startup Repair Couldn’t Repair Your PC” Error
- How to Debloat Windows 10 and 11 Without Any Third-Party Software
🛠️ Common Issues Solved with Safe Mode
You might be wondering — when should I use Safe Mode?
Here are some examples:
- Malware Removal: Some malware auto-starts with Windows. Safe Mode blocks them from running so antivirus tools can work.
- Driver Rollbacks: If a new driver breaks your display, Safe Mode lets you safely uninstall or roll back.
- System Restore: Safe Mode lets you use System Restore to roll back to a previous stable state.
- Blue Screen (BSOD) Errors: Use Safe Mode to diagnose hardware or system issues.
- Black Screen with Cursor: This often indicates explorer.exe isn’t loading — Safe Mode helps you reset shell settings.
🧩 Bonus Tip: Use msconfig to Reboot into Safe Mode (Alternative Method)
If you’re comfortable with advanced tools, you can use System Configuration (msconfig) to reboot into Safe Mode automatically:
- Press Windows + R
- Type
msconfigand press Enter - Go to the Boot tab
- Check Safe Boot, and select Minimal
- Click OK and Restart
Your PC will now boot directly into Safe Mode.
⚠️ Important: Once done, go back to
msconfigand uncheck Safe Boot before restarting again, or Windows will stay in Safe Mode forever.
🧠 FAQs
Q: Is Safe Mode available in Windows 11 Home and Pro?
Yes. Safe Mode is available across all editions of Windows 11.
Q: Can I use Safe Mode to back up files if Windows is not booting?
Absolutely. Use Safe Mode with Networking or plug in a USB drive to copy essential files.
Q: Why is my screen resolution low in Safe Mode?
Safe Mode loads only basic video drivers — that’s why the resolution looks off. It’s temporary.
Q: What if Safe Mode doesn’t work either?
In that case, you may need to boot from a Windows 11 recovery USB and attempt Startup Repair, System Restore, or a clean installation.
🧾 Disclaimer
Disclaimer: Performing force shutdowns or using Safe Mode incorrectly may cause data loss or system issues if not handled carefully. Always back up your data before making significant system changes. This guide is for educational purposes only. Proceed at your own risk.
📘 Summary
Safe Mode in Windows 11 remains one of the most effective ways to troubleshoot issues — whether you’re facing software conflicts, malware, or startup errors.
To summarize:
- Use Shift + Restart from inside Windows for easy access.
- Use Automatic Repair if Windows won’t boot.
- Choose between Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Networking, or Safe Mode with Command Prompt depending on your needs.
- Don’t forget to restart normally after your troubleshooting is complete.
With this guide, you’re now equipped to handle many of the common issues that plague Windows users — like a true tech pro!
Tags:
Windows 11 troubleshooting, how to enter safe mode, Windows recovery options, safe mode with networking, startup repair Windows 11, boot Windows in safe mode, msconfig Windows 11, Windows 11 boot options, Windows recovery screen, safe mode guide
Hashtags:
#Windows11 #SafeMode #TechTips #PCTroubleshooting #WindowsHelp #FixWindows #StartupRepair #WindowsGuide #ComputerHelp #TroubleshootingTips