Walk into any supermarket, and you’ll see barcodes on every product. For decades, barcodes have been the backbone of item identification, inventory management, and checkout systems. But as our world becomes more connected and fast-paced, a new player is quietly taking over—and it’s called RFID (Radio Frequency Identification).
Unlike barcodes, which require line-of-sight scanning, RFID can read multiple items at once, even if they’re not visible. No beeping at a scanner. No aligning. Just walk past a reader—and you’re done.
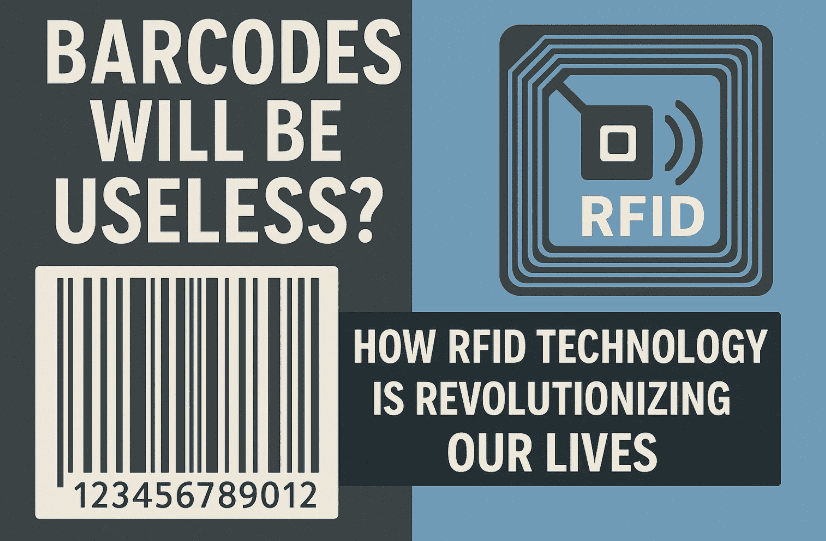
Can RFID really replace barcodes entirely? The answer is: in many industries, it already is.
In this blog, we’ll explore RFID in depth—what it is, how it works, where it’s used, and how it’s silently transforming industries ranging from retail and healthcare to transportation and security.
📡 What Is RFID?
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification—a technology that uses radio waves to identify and track items wirelessly.
Think of it like calling out a friend’s name from across a room. Even if they can’t see you, they respond. Similarly, RFID tags respond to radio signals from a reader, transmitting stored data instantly.
It’s a fast, contactless method of identification. No scanning needed. No human interaction required. And that’s what makes it so powerful.
🧩 Components of an RFID System
Before we move forward, let’s understand the two core parts of any RFID system:
1. RFID Tag
This is the smart label or chip that stores data. It contains:
- A microchip for data storage (like item ID, batch, expiry)
- An antenna to transmit the signal
There are two types of RFID tags:
- Active Tags – Have their own battery, transmit signals over long distances
- Passive Tags – No battery; activated by the RFID reader’s signal
2. RFID Reader
A device that emits radio waves and listens for responses. It:
- Detects RFID tags within range
- Reads data transmitted by the tags
- Sends that data to a computer system
Together, these components make it possible to track objects in real-time, without touching them.
🌀 How Does RFID Work?
Now that we know the parts, let’s see how they interact.
Here’s a simplified process:
- The RFID reader emits radio waves into a specific range.
- When an RFID tag enters this range, it picks up the signal.
- If it’s a passive tag, it becomes momentarily powered by the signal.
- The tag then sends its stored data back to the reader.
- The reader transmits the data to a computer or server for further processing.
This process takes milliseconds—so fast that multiple items can be scanned at once, even if buried inside boxes or behind packaging.
✅ RFID vs. Barcode: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Barcode | RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Line-of-sight required | Yes | No |
| Can scan multiple items | No (one at a time) | Yes (bulk scanning) |
| Rewritable | No | Yes (some RFID tags) |
| Hidden inside items | No | Yes |
| Cost per tag | Very low | Higher (but decreasing) |
While RFID is still more expensive than barcodes, costs are dropping fast, and many industries find the time savings and accuracy worth the investment.
🌍 Real-Life Applications of RFID
So far, we’ve done a good job understanding how RFID works. Now let’s see where it’s being used—and how it’s reshaping the world.
1. 🚗 Toll Collection (FASTag)
FASTag, used at toll plazas across India, is a classic example of RFID:
- An RFID tag on your windshield communicates with the toll reader
- Payment is deducted instantly without stopping
2. 🛍 Inventory and Retail Management
Warehouses and stores use RFID to:
- Monitor stock levels
- Track products through supply chains
- Detect theft or misplaced items
Unlike barcodes, RFID can read hundreds of tags simultaneously, even inside closed boxes.
3. 🔐 Access Control & Security
Modern offices, stadiums, and buildings issue RFID access cards:
- Employees tap or walk past scanners
- Only authorized individuals get access
- Enhances both security and efficiency
4. 🐄 Animal Tracking
Farmers and ranchers attach RFID tags to animals:
- Monitors health, vaccination, and age
- Helps in livestock management and disease control
- Tags often attached to ears, visible or embedded
5. 🚛 Supply Chain & Logistics
From production to delivery, RFID tracks:
- Packages in transit
- Storage conditions
- Delivery accuracy
This ensures real-time tracking, reduced loss, and better customer satisfaction.
6. 📚 Library Management
Books in many modern libraries have RFID tags:
- Enable faster check-in/check-out
- Help find misplaced books
- Automate inventory audits
No more scanning each barcode individually!
7. 🏃 Sports Timing
Marathon runners and cyclists wear RFID tags:
- RFID readers at start and finish lines track precise race times
- Eliminates manual stopwatch errors
8. 🅿️ Vehicle Parking Systems
Showrooms and parking lots use RFID to:
- Track test-drive vehicles
- Monitor occupied slots
- Automate entry/exit billing
9. 🏨 Hotel and Hospital Linen Management
Hospitals and hotels track:
- Bedsheets, uniforms, curtains using RFID
- Each item’s wash history, usage count
- Reduces theft, improves hygiene, and operational efficiency
10. 🚮 Waste Management in Smart Cities
Municipalities attach RFID tags to bins and garbage trucks:
- Know where trash was collected, and how often
- Monitor missed areas
- Make city waste collection more accountable and efficient
🔮 The Future of RFID: What’s Coming Next?
The use of RFID is only growing—and soon, it will become embedded in daily life like never before.
Let’s take a look at future possibilities:
📦 Smart Homes
Home appliances (like lights and ACs) may contain RFID chips that:
- Detect who’s in the room
- Auto-adjust temperature or lighting
- Learn your preferences and save energy
💊 Pharmaceutical Safety
Every medicine bottle may have an RFID tag to:
- Track production and expiry
- Prevent counterfeit drug circulation
- Alert doctors to recalled medicines
🍽 Farm-to-Table Food Tracking
From farm to your plate:
- RFID can track the entire food supply chain
- Ensure freshness, origin verification, and safety
This level of transparency can transform how we shop and eat.
⚠️ Disclaimer
While RFID technology brings immense benefits in automation, tracking, and convenience, it also raises concerns related to data privacy and surveillance. Always ensure that RFID systems in sensitive areas are implemented with proper encryption and ethical guidelines.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is RFID replacing barcodes?
Not entirely. RFID is replacing barcodes in high-volume, automated environments where speed and accuracy are critical. But for low-cost retail, barcodes still dominate due to affordability.
Q2: Can RFID tags be reused?
Yes, active RFID tags and some programmable passive tags can be reused or updated with new data.
Q3: Is RFID secure?
It depends on the implementation. Without encryption or access controls, RFID can be vulnerable to data theft or spoofing. Modern systems often use secure protocols.
Q4: How far can RFID be read from?
- Passive tags: A few centimeters to a few meters
- Active tags: Up to 100 meters or more, depending on signal strength
Q5: What industries benefit the most from RFID?
- Logistics and supply chains
- Retail and supermarkets
- Healthcare
- Livestock and agriculture
- Events and sports timing
- Public transportation
🧠 Final Thoughts
RFID isn’t just a technical upgrade—it’s a silent revolution. It’s taking over where barcodes fall short, making everything from toll collection and retail to animal tracking and hospital management smarter and faster.
And while barcodes may never fully disappear, RFID is surely taking the lead in critical industries where speed, automation, and contactless systems matter.
So next time you breeze through a toll booth, wave a card to open a door, or hear an alarm beep in a clothing store—remember, it’s not magic. It’s RFID doing its job.
Tags and Hashtags
Tags: rfid technology, rfid vs barcode, how rfid works, rfid applications, fastag technology, contactless scanning, rfid in logistics, smart city waste tracking, library rfid management, animal tracking technology, future of identification tech
Hashtags:
#RFID #RFIDTechnology #BarcodesVsRFID #SmartTracking #TechExplained #RFIDInRetail #ContactlessTech #Automation #InventoryManagement #FutureTech